The table below explains the main differences between the somatic and autonomic nervous systems.
| |
Somatic Nervous System |
Autonomic Nervous System |
| Effectors |
Skeletal muscles |
Cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands |
| Type of control |
Voluntary |
Involuntary |
| Neural pathway |
One motor neuron extends from central nervous system and synapses directly with a skeletal muscle fiber |
One motor neuron (preganglion neuron) extends from the central nervous system and synapses with another motor neuron in a ganglion; the second motor neuron (postganglion neuron) synapses with a visceral effector |
| Neurotransmitter |
Acetylcholine |
Acetylcholine or norephinephrine |
| Action of neurotransmitter on effector |
Always excitatory (causing contraction of skeletal muscle) |
May be excitatory (causing contraction of smooth muscle, increased heart rate, increased force of heart contraction, or increased secretions from glands) or inhibitory (causing relaxation of smooth muscle, decreased heart rate, or decreased secretions from glands) |
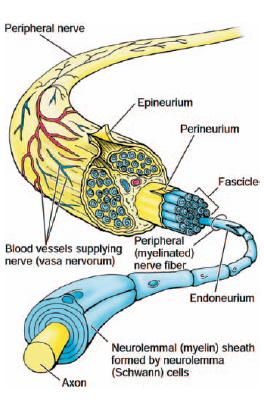
The structure of a peripheral nerve. (From Stedman’s Medical Dictionary. 27th Ed. Baltimore: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, 2000.)

