Cardiovascular disease is a generic term for diseases of the heart (cardio) and blood vessels (vascular). Some cardiovascular diseases are congenital (present at birth), while others are acquired later in life. Heart diseases affect the heart, arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle, or valves that ensure that blood in the heart is pumped in the correct direction. Examples of heart disease are coronary artery disease (diseases of the arteries, which supply the heart with blood), valvular heart disease (diseases affecting the heart valves), congenital heart disease, and heart failure. Disorders of the blood vessels include arteriosclerosis, hypertension (high blood pressure), stroke, aneurysm, venous thrombosis (formation of blood clots in a vein), and varicose veins.
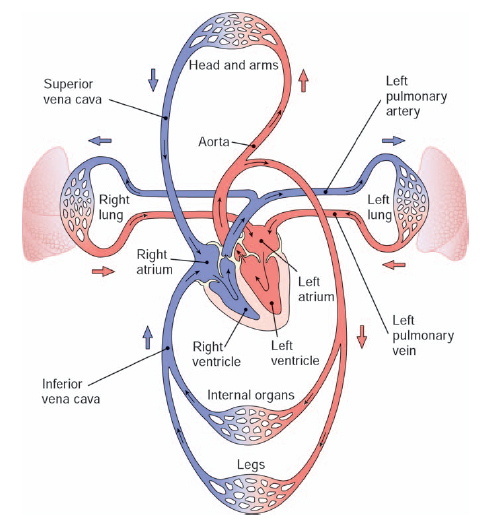
A simplified diagram of the basic cardiovascular system. (From Cohen, B. J., and Wood, D. L. Memmler’s The Human Body in Health and Disease. 9th Ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, 2000.)

