Cardiovascular SystemBlood |
What is an anticoagulant? |
An anticoagulant is any substance that prevents platelets from piling up in the inner lining (endothelium) of blood vessels. Endothelial cells naturally secrete nitric oxide and prostacyclin, which prevent platelets from sticking together. Another natural anticoagulant is heparin, which is found in basophils (a type of white blood cell) and on the surface of endothelial cells. It interferes with the process of clot formation.
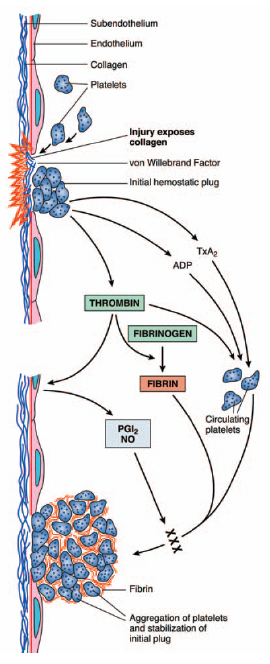
Platelet cells are the body’s tool for repairing damage through the creation of clots. (From Rubin, E., M.D., and Farber, J. L., M.D. Pathology. 3rd Ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, 1999.)
