Earth and the MoonEclipses |
How long do solar eclipses last, and how widely is a solar eclipse visible? |
The entire process of a solar eclipse, from the beginning of partial coverage until the end, usually takes about an hour. However, the totality of solar eclipse lasts at most 190 only a few minutes. Most total solar eclipses last between one hundred and two hundred seconds—just about two to three minutes. Furthermore, total solar eclipses can be observed only from narrow bands on Earth’s surface, and these bands change with each eclipse. In any given location on Earth, therefore, a total solar eclipse may appear only once every few centuries.
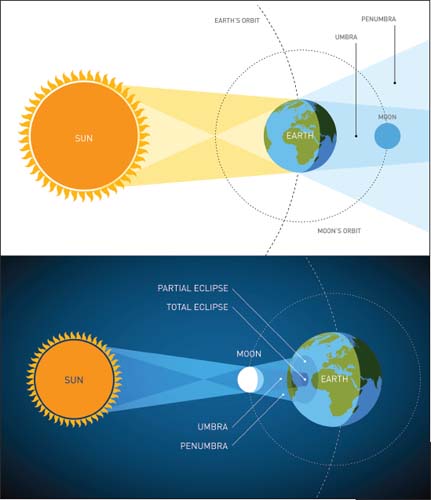
This diagram shows the relative positions of the Earth, Moon, and Sun during a lunar (top) and a solar (bottom) eclipse.
