Anatomy: Animals InsideTissue and Cells |
What are epithelial tissues? |
A tissue (from the Latin texere, meaning “to weave”) is a group of similar cells that perform a specific function. For example, the epithelial tissue, also called epithelium (from the Greek epi, meaning “on,” and thele, meaning “nipple”), covers every surface, both external and internal, of the body. The outer layer of the skin, the epidermis, is one example of epithelial tissue; other examples are the lining of the lungs, kidney tubules, and the inner surfaces of the digestive system—including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines—and the lining of parts of the respiratory system. In general, the epithelium forms a barrier, allowing the passage of certain substances while impeding the passage of other substances.
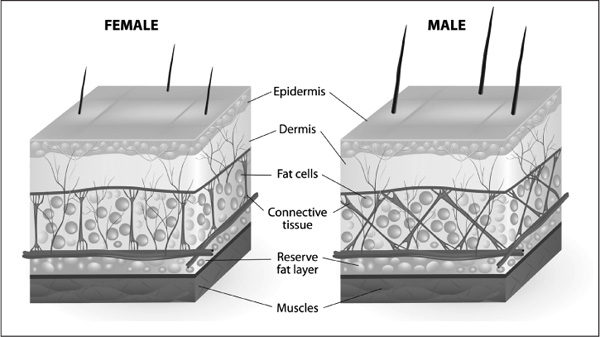
The main difference between female and male skin is that a man’ skin is thicker and tougher (more connective tissue). Also, men produce more sebum (oil), which is why they tend to have more pimple problems at puberty than women do.
