Cellular BasicsCell Responses |
What is another way cells can move? |
Not only does phagocytosis allow us to remove minute, potentially deadly body invaders, but it also is important in the maintenance of healthy tissues. Without this mechanism, harmful materials would accumulate and interfere with the body’s ability to function. A good example is the macrophages (white blood cells in the tissues) of the human spleen and liver, which dispose of more than 10,000,000,000 old (aged) blood cells a day!
Pseudopodia, often referred to as “fake feet,” are cellular extensions caused by a stretching of the cell membrane. For example, they are used by amoebas (protists) for movement and catching prey; macrophages—the white blood cells that play an important role in a human’s immune system—use pseudopodia to attack and devour invading microbes.
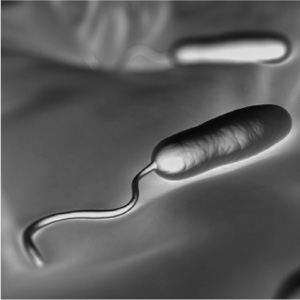
A flagella, such as the one on this sperm cell, looks like a tail and moves back and forth to propel some tiny organisms.
