Organic ChemistryStructures and Nomenclature |
What are enantiomers? |
Enantiomers are molecules that are chiral. In organic chemistry, if a carbon atom is bonded to four different atoms (or groups of elements), then we can draw two enantiomers of the molecule. Remember that the connectivity does not change, just the arrangement of the atoms in space.
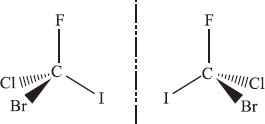
Wait—what do those dashed and wedged bonds mean?
Up to this point we’ve mostly been representing molecules as flat objects, where chemical bonds are just shown as straight lines. But molecules are not flat. In the previous question, the four halogen atoms around the central carbon form a tetrahedron. Chemists use dashed bonds to indicate that they are behind the plane of the paper, and wedged bonds come toward you, above the plane of the paper.
