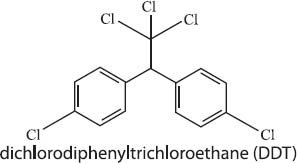
DDT, or dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, is a substance that was widely used as an insecticide until its harmful effects on human health and on wildlife became known; DDT was essentially poisoning the humans and wildlife who came into contact with it. In the context of the advent of green chemistry, DDT carries a special significance in that it helped to awaken the public to the fact that the indiscriminate use of chemicals was causing harm to the environment. News of the harmful effects of DDT was spread by Rachel Carson’s 1962 book, Silent Spring, which explained the numerous negative environmental effects of spraying DDT on crops. Knowledge of the harmful effects of DDT helped to awaken the public to the idea that releasing large amounts of relatively untested chemicals into the environment was potentially causing damage to humans and wildlife. DDT was officially banned in the U.S. in 1972.