BiochemistryMolecules of Life |
What is a glycosidic linkage? |
A glycosidic linkage is the chemical bond that bonds a carbohydrate to another carbohydrate molecule (or to another species). Glycosidic linkages are what hold together all of the individual glucose monomers that make up glycogen or starch. The figure below shows a glycosidic linkage.
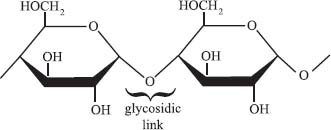
The enzymes that catalyze the breakage glycosidic linkages are called glycoside hydrolases. These are necessary to allow for glucose to be released from storage. The enzymes responsible for forming the linkages are called glycosyltransferases.
