Analytical ChemistryElectrochemistry |
What is an electrochemical cell? |
One common example of a redox reaction in electrochemistry involves the transfer of electrons from zinc (Zn) metal to copper (Cu) ions in an electrochemical cell.
Zinc (Zn) gives up electrons more readily than copper (Cu), so electrons spontaneously transfer from the Zn metal to the Cu metal, depositing Zn2+ ions into the solution and causing Cu metal to come out of the solution and onto the solid. This process releases energy, which can be used to drive external processes (such as powering a lightbulb, for example).
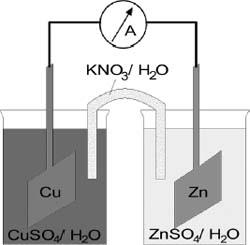
In this example of an electrochemical cell, a piece of zinc (Zn) and a piece of copper (Cu) are placed in solutions of zinc sulfate and copper sulfate, respectively, connected by a salt bridge of potassium nitrate. Electrons are given up by the zinc anode and transferred to the copper cathode, generating an electrical current.
