BiochemistryMetabolism and Other Biochemical Reactions |
What is cooperativity? |
Cooperativity describes how the binding affinity at one site of a protein affects the binding affinity at another site. In hemoglobin, for example, there are four sites at which oxygen molecules can bind. After the first oxygen molecule binds, conformational changes take place in the rest of the protein that increase the binding affinity at the other sites. The second oxygen is then able to bind even more easily, and the third and fourth even more easily yet. This gives rise to a sigmoidal-curved shape in a plot of the fraction of hemoglobin bound by O2 versus the partial pressure of O2 (see illustration).
Similar binding curves result in other examples of cooperativity, though the example of hemoglobin is probably the most commonly discussed example of the phenomenon.
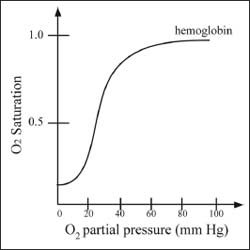
A graph describing cooperativity in hemoglobin.
