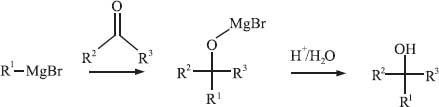
The Grignard reaction is one of the most well-known and powerful reactions in organo-metallic synthesis, primarily due to its ability to readily form new carbon-carbon bonds. In this reaction, a Grignard reagent reacts by adding to a carbonyl functional group of an aldehyde or ketone and forms a new carbon-carbon bond at the carbonyl carbon. Grignard reagents, which are organometallic species that carry out the Grignard reaction, are typically formed by adding magnesium metal to an alkyl or aryl halide (R1-Br in the scheme below). The discovery of this important reaction was awarded with a Nobel Prize in 1912, and the reaction is actually also named after the French chemist François Auguste Victor Grignard, who discovered it.