BiochemistryMolecules of Life |
What is the basic structure of an amino acid? |
The basic structure of an amino acid is shown below.
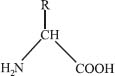
Each amino acid has an amine (NH2) group, a central carbon atom known as the alpha carbon, a side chain (denoted R), and a carboxylic acid (COOH) group. The amine groups and carboxylic acid groups of amino acids can be joined in a chain to form polymers of amino acids, known as peptides. Two amino acids form a dipeptide, three form a tripeptide, and chains of four or more amino acids are commonly referred to as polypeptides. Long polypeptides fold into specific conformations, which is what makes up a protein.
