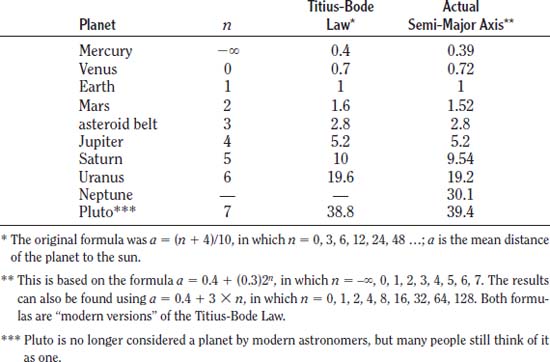
The Titius-Bode Law was developed by German astronomer Johann Daniel Titius (1729–1796); Titius’s idea was brought to the forefront by German astronomer Johann Elert Bode (1747–1826). The law actually represents a simple mathematical rule that allows one to determine the distances (also called the semi-major axis) of the planets in astronomical units. It is determined using the equation a = 0.4 + (0.3)2n, in which n is an integer and a is the astronomical unit. Interestingly enough, most of the planets—and even the asteroids in the Asteroid Belt—adhere to the law. The only exception is Neptune, the second-to-last planet in our solar system.