Health and MedicineHealth Hazards and Risks |
How is body mass index (BMI) calculated? |
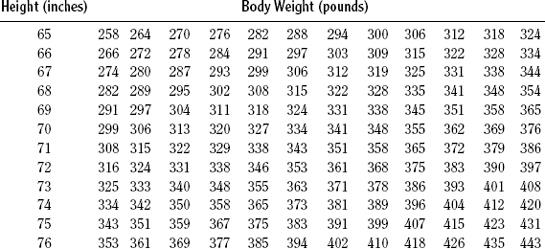
The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), in cooperation with the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, released guidelines for weight for adults in 1998. These guidelines define degrees of overweight and obesity in terms of body mass index (BMI). Body mass index is based on weight and height and is strongly correlated with total body fat content. It is used to assess an individual’s weight-related level of risk for heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure. Very muscular individuals, such as athletes, may have a high BMI without health risks.
185 pounds × 703 = 130,055
702 = 4,900
130,055/4,900 = 26.5
| Evaluating BMI in Adults | |
| BMI | Weight Status |
| Below 18.5 | Underweight |
| 18.5–24.9 | Normal |
| 25.0–29.9 | Overweight |
| 30.0 and above | Obese |
| Evaluating BMI in Children and Teenagers Ages 2 to 20 | |
| BMI | Weight Status |
| BMI-for-age < 5th=""> | Underweight |
| BMI-for-age 5th percentile to < 85th=""> | Normal |
| BMI-for-age 85th percentile to < 95th=""> | At risk of being overweight |
| BMI-for-age < 95th=""> | Overweight |