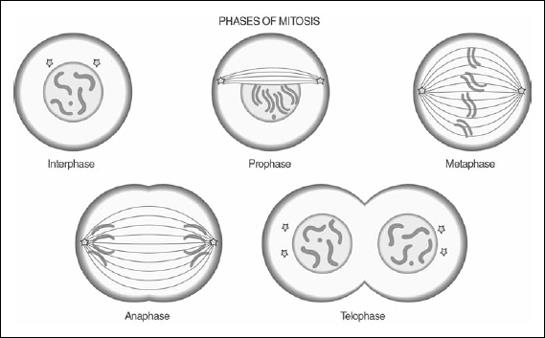
Mitosis involves the replication of DNA and its separation into two new daughter cells which are genetically identical to the parent cell. While only four phases of mitosis are often listed, the entire process is actually composed of six phases:
- Interphase: Involves extensive preparation for the division process
- Prophase: The condensation of chromosomes; the nuclear membrane disappears; formation of the spindle apparatus; chromosomes attach to spindle fibers
- Metaphase: Chromosomes, attached by spindle fibers, align along the midline of a cell
- Anaphase: The entromere splits and chromatids move apart
- Telophase: The nuclear membrane reforms around newly divided chromosomes
- Cytokinesis: The division of cytoplasm, cell membranes, and organelles occur. In plants, a new cell wall forms