Weather in SpaceThe Magnetic Field |
Why is Earth’s magnetic field important to life on Earth? |
Earth’s magnetic field extends out into space, creating a structure called a magnetosphere, which surrounds our planet. When the magnetosphere is hit by charged particles from space, such as from the solar wind or from a coronal mass ejection, it deflects these particles away from Earth’s surface, significantly reducing the amount that strikes life forms down on Earth’s surface. This protects us from the hazards of being hit by too many such particles.
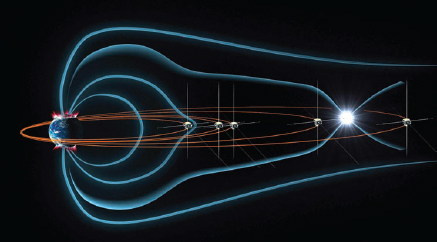
A graphic from NASA depicts the THEMIS (Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms) mission to study the Earth’s magnetic fields (blue lines) and substorms (aurora that result from intense space storms).THEMIS’s orbit changes to varying degrees in order to better pinpoint the location of substorms. (NASA)
